-
Posts
9903 -
تاريخ الانضمام
-
تاريخ اخر زياره
-
Days Won
404
نوع المحتوي
المنتدى
مكتبة الموقع
معرض الصور
المدونات
الوسائط المتعددة
كل منشورات العضو jjafferr
-

ارجو المساعدة وضع كود يقوم بإخراج القيم الثلاثة الكبرى
jjafferr replied to khapozed's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
حياك الله أخوي عبدالرحمن بس السؤال ، اي الطريقتين صح ، لأن الوسط والاصغر يملكان نفس القيمة ، ولكن اسم الحقل مختلف ، وطبعا السؤال كان في فرز الارقام وليس فرز اسماء الحقول جعفر -

ارجو المساعدة وضع كود يقوم بإخراج القيم الثلاثة الكبرى
jjafferr replied to khapozed's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
تفضل عملت لك طريقتين: الاولى باستخدام الجدول المؤقت tbl_Temp ، والطريقة الثانية عن طريق الكود ووحدة نمطية: . الجزء الاول من الكود لطريقة الجدول المؤقت ، والطريقة الثانية للكود: Function Sort_It() Dim rst As DAO.Recordset Dim rstT As DAO.Recordset 'clear tbl_Temp CurrentDb.Execute ("Delete * From tbl_Temp") 'DoCmd.RunSQL ("Delete * From tbl_Temp") Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("Select * From [درجات] Where [Auto_ID]=" & Me.Auto_ID) Set rstT = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("Select * From tbl_Temp") For ii = 1 To rst.Fields.Count - 1 'MsgBox rst(ii).Name & vbCrLf & rst(ii) rstT.AddNew rstT!iNumber = rst(ii) rstT!iField = rst(ii).Name rstT.Update Next ii 'DoCmd.OpenQuery "qry_Sort_it" Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("Select * From tbl_Temp Order By iNumber Desc") rst.MoveLast: rst.MoveFirst Me.L1 = rst!iNumber & vbCrLf & rst!iField rst.MoveNext Me.L2 = rst!iNumber & vbCrLf & rst!iField rst.MoveNext Me.L3 = rst!iNumber & vbCrLf & rst!iField rst.Close: Set rst = Nothing rstT.Close: Set rstT = Nothing End Function Private Sub Form_Current() Call Sort_It Me.L11 = "" Me.L22 = "" Me.L33 = "" Call cmd_Sort_Click End Sub Private Sub cmd_Sort_Click() Dim rst As DAO.Recordset Dim InputArray() As Variant Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("Select * From [درجات] Where [Auto_ID]=" & Me.Auto_ID) ReDim InputArray(rst.Fields.Count - 1) 'make the array For ii = 1 To rst.Fields.Count - 1 'MsgBox rst(ii).Name & vbCrLf & rst(ii) InputArray(ii) = rst(ii) Next ii 'call the sorting array Call QSortInPlace(InputArray, , , True) 'display the numbers For ii = 0 To rst.Fields.Count - 2 'then sorted numbers For jj = 0 To rst.Fields.Count - 2 'match the numbers, then display its field name If InputArray(ii) = rst(jj) Then 'MsgBox InputArray(ii) & vbCrLf & rst(jj).Name 'don't repeat the same field name If InStr(Me.L11, rst(jj).Name) > 0 Or InStr(Me.L22, rst(jj).Name) > 0 Then GoTo 2 If Len(Me.L11 & "") = 0 Then Me.L11 = InputArray(ii) & vbCrLf & rst(jj).Name ElseIf Len(Me.L22 & "") = 0 Then Me.L22 = InputArray(ii) & vbCrLf & rst(jj).Name ElseIf Len(Me.L33 & "") = 0 Then Me.L33 = InputArray(ii) & vbCrLf & rst(jj).Name End If End If 2: Next jj Next ii End Sub . واما الوحدة النمطية التي استخدمتها للفرز: Option Compare Database Public Function QSortInPlace( _ ByRef InputArray As Variant, _ Optional ByVal LB As Long = -1&, _ Optional ByVal UB As Long = -1&, _ Optional ByVal Descending As Boolean = False, _ Optional ByVal CompareMode As VbCompareMethod = vbTextCompare, _ Optional ByVal NoAlerts As Boolean = False) As Boolean ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' QSortInPlace ' ' This function sorts the array InputArray in place -- this is, the original array in the ' calling procedure is sorted. It will work with either string data or numeric data. ' It need not sort the entire array. You can sort only part of the array by setting the LB and ' UB parameters to the first (LB) and last (UB) element indexes that you want to sort. ' LB and UB are optional parameters. If omitted LB is set to the LBound of InputArray, and if ' omitted UB is set to the UBound of the InputArray. If you want to sort the entire array, ' omit the LB and UB parameters, or set both to -1, or set LB = LBound(InputArray) and set ' UB to UBound(InputArray). ' ' By default, the sort method is case INSENSTIVE (case doens't matter: "A", "b", "C", "d"). ' To make it case SENSITIVE (case matters: "A" "C" "b" "d"), set the CompareMode argument ' to vbBinaryCompare (=0). If Compare mode is omitted or is any value other than vbBinaryCompare, ' it is assumed to be vbTextCompare and the sorting is done case INSENSITIVE. ' ' The function returns TRUE if the array was successfully sorted or FALSE if an error ' occurred. If an error occurs (e.g., LB > UB), a message box indicating the error is ' displayed. To suppress message boxes, set the NoAlerts parameter to TRUE. ' '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' MODIFYING THIS CODE: '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' If you modify this code and you call "Exit Procedure", you MUST decrment the RecursionLevel ' variable. E.g., ' If SomethingThatCausesAnExit Then ' RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 ' Exit Function ' End If ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' ' Note: If you coerce InputArray to a ByVal argument, QSortInPlace will not be ' able to reference the InputArray in the calling procedure and the array will ' not be sorted. ' ' This function uses the following procedures. These are declared as Private procedures ' at the end of this module: ' IsArrayAllocated ' IsSimpleDataType ' IsSimpleNumericType ' QSortCompare ' NumberOfArrayDimensions ' ReverseArrayInPlace ' ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim Temp As Variant Dim Buffer As Variant Dim CurLow As Long Dim CurHigh As Long Dim CurMidpoint As Long Dim Ndx As Long Dim pCompareMode As VbCompareMethod ''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Set the default result. ''''''''''''''''''''''''' QSortInPlace = False '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' This variable is used to determine the level ' of recursion (the function calling itself). ' RecursionLevel is incremented when this procedure ' is called, either initially by a calling procedure ' or recursively by itself. The variable is decremented ' when the procedure exits. We do the input parameter ' validation only when RecursionLevel is 1 (when ' the function is called by another function, not ' when it is called recursively). '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Static RecursionLevel As Long '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Keep track of the recursion level -- that is, how many ' times the procedure has called itself. ' Carry out the validation routines only when this ' procedure is first called. Don't run the ' validations on a recursive call to the ' procedure. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel + 1 If RecursionLevel = 1 Then '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure InputArray is an array. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(InputArray) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The InputArray parameter is not an array." End If ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' InputArray is not an array. Exit with a False result. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test LB and UB. If < 0 then set to LBound and UBound ' of the InputArray. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If LB < 0 Then LB = LBound(InputArray) End If If UB < 0 Then UB = UBound(InputArray) End If Select Case NumberOfArrayDimensions(InputArray) Case 0 '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Zero dimensions indicates an unallocated ' dynamic array. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The InputArray is an empty, unallocated array." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function Case 1 '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We sort ONLY single dimensional arrays. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Case Else '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We sort ONLY single dimensional arrays. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The InputArray is multi-dimensional." & _ "QSortInPlace works only on single-dimensional arrays." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End Select ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure that InputArray is an array of simple data ' types, not other arrays or objects. This tests ' the data type of only the first element of ' InputArray. If InputArray is an array of Variants, ' subsequent data types may not be simple data types ' (e.g., they may be objects or other arrays), and ' this may cause QSortInPlace to fail on the StrComp ' operation. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsSimpleDataType(InputArray(LBound(InputArray))) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "InputArray is not an array of simple data types." RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End If End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' ensure that the LB parameter is valid. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Select Case LB Case Is < LBound(InputArray) If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The LB lower bound parameter is less than the LBound of the InputArray" End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function Case Is > UBound(InputArray) If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The LB lower bound parameter is greater than the UBound of the InputArray" End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function Case Is > UB If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The LB lower bound parameter is greater than the UB upper bound parameter." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End Select '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' ensure the UB parameter is valid. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Select Case UB Case Is > UBound(InputArray) If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The UB upper bound parameter is greater than the upper bound of the InputArray." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function Case Is < LBound(InputArray) If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The UB upper bound parameter is less than the lower bound of the InputArray." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function Case Is < LB If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "the UB upper bound parameter is less than the LB lower bound parameter." End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End Select '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' if UB = LB, we have nothing to sort, so get out. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If UB = LB Then QSortInPlace = True RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 Exit Function End If End If ' RecursionLevel = 1 '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure that CompareMode is either vbBinaryCompare or ' vbTextCompare. If it is neither, default to vbTextCompare. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If (CompareMode = vbBinaryCompare) Or (CompareMode = vbTextCompare) Then pCompareMode = CompareMode Else pCompareMode = vbTextCompare End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Begin the actual sorting process. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' CurLow = LB CurHigh = UB If LB = 0 Then CurMidpoint = ((LB + UB) \ 2) + 1 Else CurMidpoint = (LB + UB) \ 2 ' note integer division (\) here End If Temp = InputArray(CurMidpoint) Do While (CurLow <= CurHigh) Do While QSortCompare(V1:=InputArray(CurLow), V2:=Temp, CompareMode:=pCompareMode) < 0 CurLow = CurLow + 1 If CurLow = UB Then Exit Do End If Loop Do While QSortCompare(V1:=Temp, V2:=InputArray(CurHigh), CompareMode:=pCompareMode) < 0 CurHigh = CurHigh - 1 If CurHigh = LB Then Exit Do End If Loop If (CurLow <= CurHigh) Then Buffer = InputArray(CurLow) InputArray(CurLow) = InputArray(CurHigh) InputArray(CurHigh) = Buffer CurLow = CurLow + 1 CurHigh = CurHigh - 1 End If Loop If LB < CurHigh Then QSortInPlace InputArray:=InputArray, LB:=LB, UB:=CurHigh, _ Descending:=Descending, CompareMode:=pCompareMode, NoAlerts:=True End If If CurLow < UB Then QSortInPlace InputArray:=InputArray, LB:=CurLow, UB:=UB, _ Descending:=Descending, CompareMode:=pCompareMode, NoAlerts:=True End If ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' If Descending is True, reverse the ' order of the array, but only if the ' recursion level is 1. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If Descending = True Then If RecursionLevel = 1 Then ReverseArrayInPlace2 InputArray, LB, UB End If End If RecursionLevel = RecursionLevel - 1 QSortInPlace = True End Function Public Function QSortCompare(V1 As Variant, V2 As Variant, _ Optional CompareMode As VbCompareMethod = vbTextCompare) As Long ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' QSortCompare ' This function is used in QSortInPlace to compare two elements. If ' V1 AND V2 are both numeric data types (integer, long, single, double) ' they are converted to Doubles and compared. If V1 and V2 are BOTH strings ' that contain numeric data, they are converted to Doubles and compared. ' If either V1 or V2 is a string and does NOT contain numeric data, both ' V1 and V2 are converted to Strings and compared with StrComp. ' ' The result is -1 if V1 < V2, ' 0 if V1 = V2 ' 1 if V1 > V2 ' For text comparisons, case sensitivity is controlled by CompareMode. ' If this is vbBinaryCompare, the result is case SENSITIVE. If this ' is omitted or any other value, the result is case INSENSITIVE. ' ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim D1 As Double Dim D2 As Double Dim S1 As String Dim S2 As String Dim Compare As VbCompareMethod '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test CompareMode. Any value other than ' vbBinaryCompare will default to vbTextCompare. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If CompareMode = vbBinaryCompare Or CompareMode = vbTextCompare Then Compare = CompareMode Else Compare = vbTextCompare End If ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' If either V1 or V2 is either an array or ' an Object, raise a error 13 - Type Mismatch. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(V1) = True Or IsArray(V2) = True Then Err.Raise 13 Exit Function End If If IsObject(V1) = True Or IsObject(V2) = True Then Err.Raise 13 Exit Function End If If IsSimpleNumericType(V1) = True Then If IsSimpleNumericType(V2) = True Then ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' If BOTH V1 and V2 are numeric data ' types, then convert to Doubles and ' do an arithmetic compare and ' return the result. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' D1 = CDbl(V1) D2 = CDbl(V2) If D1 = D2 Then QSortCompare = 0 Exit Function End If If D1 < D2 Then QSortCompare = -1 Exit Function End If If D1 > D2 Then QSortCompare = 1 Exit Function End If End If End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Either V1 or V2 was not numeric data type. ' Test whether BOTH V1 AND V2 are numeric ' strings. If BOTH are numeric, convert to ' Doubles and do a arithmetic comparison. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsNumeric(V1) = True And IsNumeric(V2) = True Then D1 = CDbl(V1) D2 = CDbl(V2) If D1 = D2 Then QSortCompare = 0 Exit Function End If If D1 < D2 Then QSortCompare = -1 Exit Function End If If D1 > D2 Then QSortCompare = 1 Exit Function End If End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Either or both V1 and V2 was not numeric ' string. In this case, convert to Strings ' and use StrComp to compare. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' S1 = CStr(V1) S2 = CStr(V2) QSortCompare = StrComp(S1, S2, Compare) End Function Public Function NumberOfArrayDimensions(Arr As Variant) As Integer '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' NumberOfArrayDimensions ' This function returns the number of dimensions of an array. An unallocated dynamic array ' has 0 dimensions. This condition can also be tested with IsArrayEmpty. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim Ndx As Integer Dim Res As Integer On Error Resume Next ' Loop, increasing the dimension index Ndx, until an error occurs. ' An error will occur when Ndx exceeds the number of dimension ' in the array. Return Ndx - 1. Do Ndx = Ndx + 1 Res = UBound(Arr, Ndx) Loop Until Err.Number <> 0 NumberOfArrayDimensions = Ndx - 1 End Function Public Function ReverseArrayInPlace(InputArray As Variant, _ Optional NoAlerts As Boolean = False) As Boolean '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' ReverseArrayInPlace ' This procedure reverses the order of an array in place -- this is, the array variable ' in the calling procedure is sorted. An error will occur if InputArray is not an array, 'if it is an empty, unallocated array, or if the number of dimensions is not 1. ' ' NOTE: Before calling the ReverseArrayInPlace procedure, consider if your needs can ' be met by simply reading the existing array in reverse order (Step -1). If so, you can save ' the overhead added to your application by calling this function. ' ' The function returns TRUE if the array was successfully reversed, or FALSE if ' an error occurred. ' ' If an error occurred, a message box is displayed indicating the error. To suppress ' the message box and simply return FALSE, set the NoAlerts parameter to TRUE. ' ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim Temp As Variant Dim Ndx As Long Dim Ndx2 As Long Dim OrigN As Long Dim NewN As Long Dim NewArr() As Variant '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Set the default return value. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ReverseArrayInPlace = False ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure we have an array ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(InputArray) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The InputArray parameter is not an array." End If Exit Function End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test the number of dimensions of the ' InputArray. If 0, we have an empty, ' unallocated array. Get out with ' an error message. If greater than ' one, we have a multi-dimensional ' array, which is not allowed. Only ' an allocated 1-dimensional array is ' allowed. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Select Case NumberOfArrayDimensions(InputArray) Case 0 ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Zero dimensions indicates an unallocated ' dynamic array. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array is an empty, unallocated array." End If Exit Function Case 1 ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We can reverse ONLY a single dimensional ' arrray. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Case Else ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We can reverse ONLY a single dimensional ' arrray. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array multi-dimensional. ReverseArrayInPlace works only " & _ "on single-dimensional arrays." End If Exit Function End Select ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure that we have only simple data types, ' not an array of objects or arrays. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsSimpleDataType(InputArray(LBound(InputArray))) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array contains arrays, objects, or other complex data types." & vbCrLf & _ "ReverseArrayInPlace can reverse only arrays of simple data types." Exit Function End If End If ReDim NewArr(LBound(InputArray) To UBound(InputArray)) NewN = UBound(NewArr) For OrigN = LBound(InputArray) To UBound(InputArray) NewArr(NewN) = InputArray(OrigN) NewN = NewN - 1 Next OrigN For NewN = LBound(NewArr) To UBound(NewArr) InputArray(NewN) = NewArr(NewN) Next NewN ReverseArrayInPlace = True End Function Public Function ReverseArrayInPlace2(InputArray As Variant, _ Optional LB As Long = -1, Optional UB As Long = -1, _ Optional NoAlerts As Boolean = False) As Boolean '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' ReverseArrayInPlace2 ' This reverses the order of elements in InputArray. To reverse the entire array, omit or ' set to less than 0 the LB and UB parameters. To reverse only part of tbe array, set LB and/or ' UB to the LBound and UBound of the sub array to be reversed. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim N As Long Dim Temp As Variant Dim Ndx As Long Dim Ndx2 As Long Dim OrigN As Long Dim NewN As Long Dim NewArr() As Variant '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Set the default return value. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ReverseArrayInPlace2 = False ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure we have an array ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(InputArray) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The InputArray parameter is not an array." End If Exit Function End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test the number of dimensions of the ' InputArray. If 0, we have an empty, ' unallocated array. Get out with ' an error message. If greater than ' one, we have a multi-dimensional ' array, which is not allowed. Only ' an allocated 1-dimensional array is ' allowed. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Select Case NumberOfArrayDimensions(InputArray) Case 0 ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Zero dimensions indicates an unallocated ' dynamic array. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array is an empty, unallocated array." End If Exit Function Case 1 ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We can reverse ONLY a single dimensional ' arrray. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Case Else ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We can reverse ONLY a single dimensional ' arrray. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array multi-dimensional. ReverseArrayInPlace works only " & _ "on single-dimensional arrays." End If Exit Function End Select ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Ensure that we have only simple data types, ' not an array of objects or arrays. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsSimpleDataType(InputArray(LBound(InputArray))) = False Then If NoAlerts = False Then MsgBox "The input array contains arrays, objects, or other complex data types." & vbCrLf & _ "ReverseArrayInPlace can reverse only arrays of simple data types." Exit Function End If End If If LB < 0 Then LB = LBound(InputArray) End If If UB < 0 Then UB = UBound(InputArray) End If For N = LB To (LB + ((UB - LB - 1) \ 2)) Temp = InputArray(N) InputArray(N) = InputArray(UB - (N - LB)) InputArray(UB - (N - LB)) = Temp Next N ReverseArrayInPlace2 = True End Function Public Function IsSimpleNumericType(V As Variant) As Boolean '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' IsSimpleNumericType ' This returns TRUE if V is one of the following data types: ' vbBoolean ' vbByte ' vbCurrency ' vbDate ' vbDecimal ' vbDouble ' vbInteger ' vbLong ' vbSingle ' vbVariant if it contains a numeric value ' It returns FALSE for any other data type, including any array ' or vbEmpty. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsSimpleDataType(V) = True Then Select Case VarType(V) Case vbBoolean, _ vbByte, _ vbCurrency, _ vbDate, _ vbDecimal, _ vbDouble, _ vbInteger, _ vbLong, _ vbSingle IsSimpleNumericType = True Case vbVariant If IsNumeric(V) = True Then IsSimpleNumericType = True Else IsSimpleNumericType = False End If Case Else IsSimpleNumericType = False End Select Else IsSimpleNumericType = False End If End Function Public Function IsSimpleDataType(V As Variant) As Boolean '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' IsSimpleDataType ' This function returns TRUE if V is one of the following ' variable types (as returned by the VarType function: ' vbBoolean ' vbByte ' vbCurrency ' vbDate ' vbDecimal ' vbDouble ' vbEmpty ' vbError ' vbInteger ' vbLong ' vbNull ' vbSingle ' vbString ' vbVariant ' ' It returns FALSE if V is any one of the following variable ' types: ' vbArray ' vbDataObject ' vbObject ' vbUserDefinedType ' or if it is an array of any type. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' On Error Resume Next '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test if V is an array. We can't just use VarType(V) = vbArray ' because the VarType of an array is vbArray + VarType(type ' of array element). E.g, the VarType of an Array of Longs is ' 8195 = vbArray + vbLong. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(V) = True Then IsSimpleDataType = False Exit Function End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' We must also explicitly check whether V is an object, rather ' relying on VarType(V) to equal vbObject. The reason is that ' if V is an object and that object has a default proprety, VarType ' returns the data type of the default property. For example, if ' V is an Excel.Range object pointing to cell A1, and A1 contains ' 12345, VarType(V) would return vbDouble, the since Value is ' the default property of an Excel.Range object and the default ' numeric type of Value in Excel is Double. Thus, in order to ' prevent this type of behavior with default properties, we test ' IsObject(V) to see if V is an object. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsObject(V) = True Then IsSimpleDataType = False Exit Function End If ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Test the value returned by VarType. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Select Case VarType(V) Case vbArray, vbDataObject, vbObject, vbUserDefinedType ''''''''''''''''''''''' ' not simple data types ''''''''''''''''''''''' IsSimpleDataType = False Case Else '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' otherwise it is a simple data type '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' IsSimpleDataType = True End Select End Function Public Function IsArrayAllocated(Arr As Variant) As Boolean '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' IsArrayAllocated ' Returns TRUE if the array is allocated (either a static array or a dynamic array that has been ' sized with Redim) or FALSE if the array has not been allocated (a dynamic that has not yet ' been sized with Redim, or a dynamic array that has been Erased). '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' Dim N As Long ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' If Arr is not an array, return FALSE and get out. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' If IsArray(Arr) = False Then IsArrayAllocated = False Exit Function End If '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Try to get the UBound of the array. If the array has not been allocated, ' an error will occur. Test Err.Number to see if an error occured. '''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' On Error Resume Next N = UBound(Arr, 1) If Err.Number = 0 Then ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' No error. Array has been allocated. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' IsArrayAllocated = True Else ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' ' Error. Unallocated array. ''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''' IsArrayAllocated = False End If End Function جعفر 281.1جديد.mdb.zip -
وعليكم السلام أخي الرجاء فتح موضوع خاص بسؤالك ، لأنه لا علاقة بين سؤالك وموضوعي هذا واهلا وسهلا بك في المنتدى جعفر
-

ارجو المساعدة وضع كود يقوم بإخراج القيم الثلاثة الكبرى
jjafferr replied to khapozed's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
وعليكم السلام ممكن تخبرنا عن استعمال البرنامج ، فالطريقة اول مرة اسمع بيها جعفر -
وعليكم السلام بالنسبة لموضوع تحويل اللغة ، انظر هذا الرابط للأستاذ علي المصري: http://www.officena.net/ib/topic/64622-كتابة-اللغة-في-مربع-نص-على-حسب-اختيار-المستخدم-من-القائمة-المنسدلة/?do=findComment&comment=420711 اعمل زر لكل لغة تريدها ، ولما يشتغل البرنامج ، ارفق البرنامج ، ونحن ان شاء الله نساعدك على الازرار جعفر
-
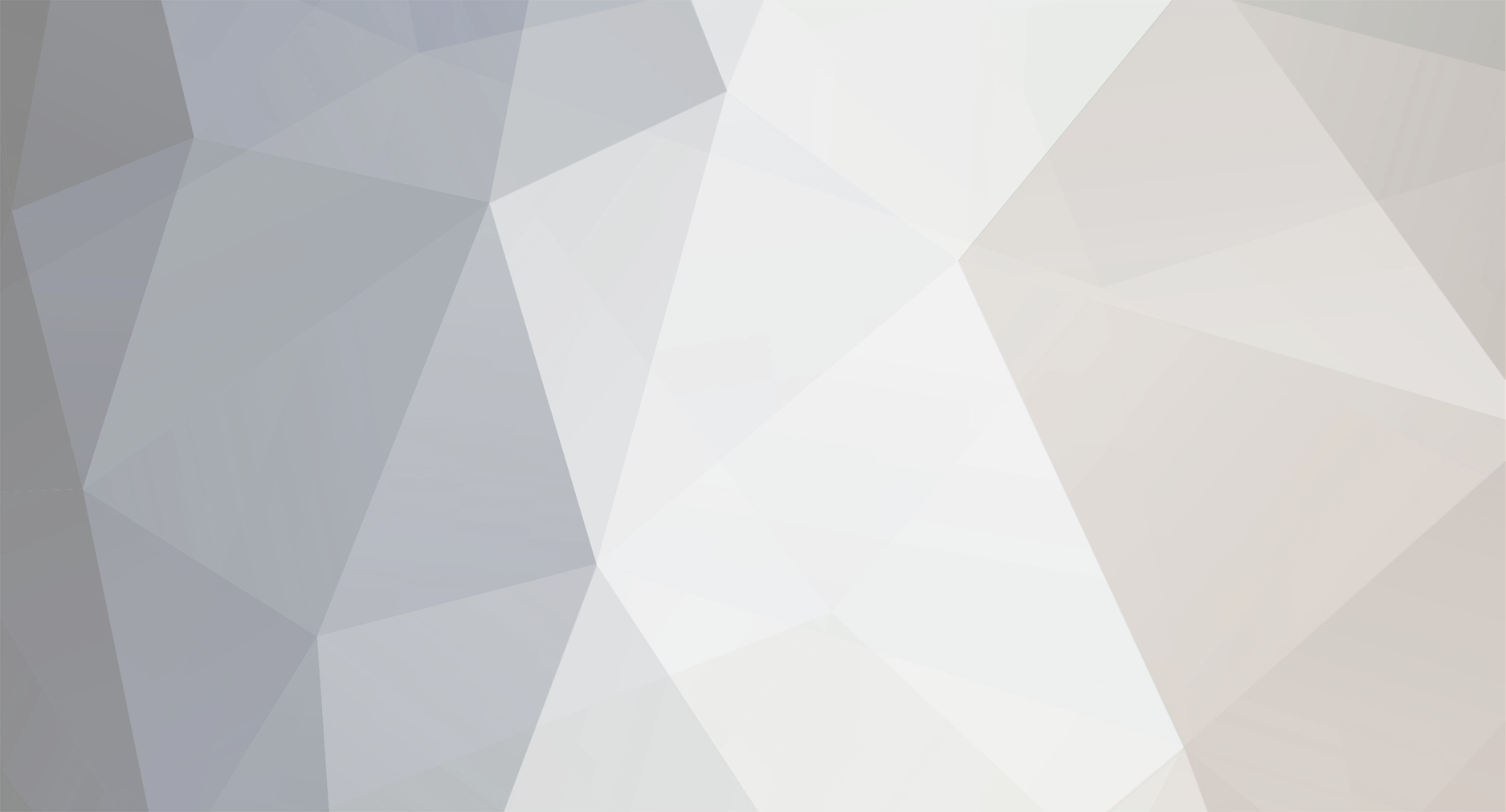
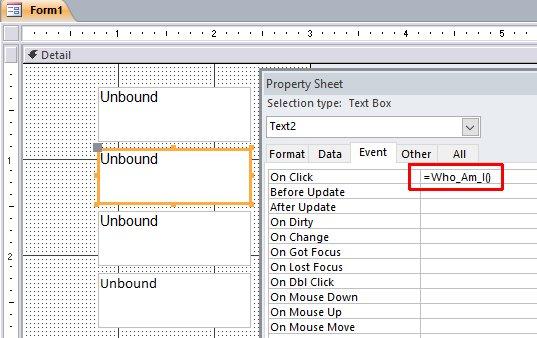
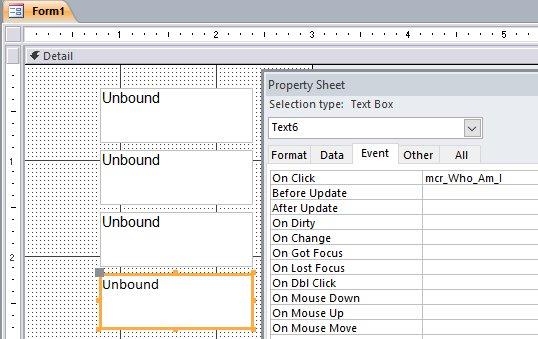
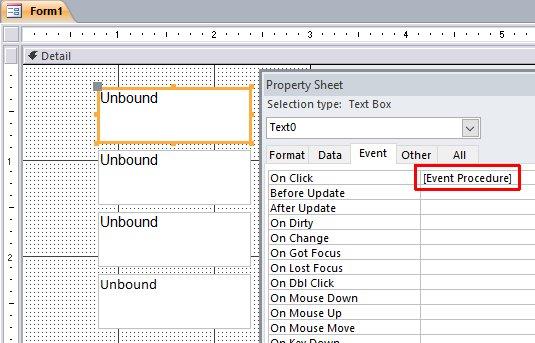
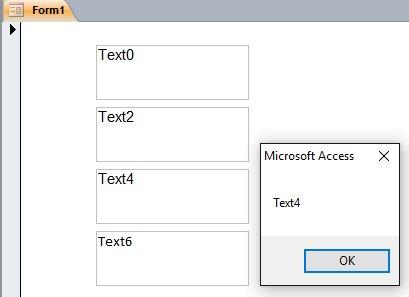
وعليكم السلام وبعد إذن أخي ابوخليل هنا اجمع جميع الطرق اللي تخطر على بالي ، وهي 4 طرق 1. طريقة أخي ابوخليل: Private Sub Text0_Click() Me.Text0 = Me.Text0.Name End Sub . الطرق الثلاث الباقية تعتمد على الوحدة النمطية: Option Compare Database Function Who_Am_I() Dim frm As Access.Form Dim ctl As Access.Control Set frm = Screen.ActiveForm 'get the active Form Name Set ctl = Screen.ActiveControl 'get the active Control (in our case it was a field) name 'The way we address a Field in another Form, 'like this: Forms!FormName!FieldName 'so we have to do it here similarly, 'this will send the field name to the active Field in the active Form Forms(frm.Name)(ctl.Name) = ctl.Name 'this will return the Funtion Who_Am_I value to the variable that called it Who_Am_I = ctl.Name End Function 2. ننادي الوحدة النمطية مباشرة (لاحظ علامة = ) ، ولا يوجد كود محلي في VBA : . 3. نعمل كود محلي ، والذي ينادي الوحدة النمطية: Private Sub Text4_Click() 'this way will get the field name from the Function Who_Am_I 'and it will place the value in the Field in the Form Call Who_Am_I 'this way will get the field name from the Function Who_Am_I 'and it will place the value in the Field in the Form 'and it WILL place the Field name in the variable A, so that we can use it A = Who_Am_I MsgBox A End Sub . وبما اننا نادينا الوحدة النمطية Who_Am_I عن طريق المتغير A ، فاصبح المتغير A لديه نتيجة/قيمة الوحدة النمطية ، وعليه نستطيع ان نستخدم هذه القيمة كيف نشاء في الكود ، فمثلا استخدمناها لإعطاءنا رسالة بإسم الحقل ، والنتيجة: . 4. نعمل ماكرو ، ونجعل الماكرو ينادي الوحدة النمطية: . (لاحظ مافي علامة = ) ، ولا يوجد كود محلي في VBA: . جعفر 280.db2016.accdb.zip
-
السلام عليكم أخي الشمال قبل ان اضع الحل اعلاه ، فكرت وبحثت كثيرا ، لكن الحلول لم اقتنع بها ، وعلى العموم اليك حلول اثنين: 1. ان تعمل زرين في النموذج ، واحد لمعاينة التقرير (ولا يستطيع المستخدم من خلالها طباعة التقرير لأنه لن يكون فيه رقم وصل) ، وواحد للطباعة مباشرة (وتضع كود رقم الوصل في النموذج ، بحيث يأخذ التقرير رقم الوصل من النموذج) أ- ان لا تسمح للمستخدم ان يطبع التقرير اثناء المعاينة (واليك الصعوبات وخطوات الحل): عند معاينة التقرير ، يستطيع المستخدم ان يطبع التقرير من شريط الادوات عن طريق ايقونة الطباعة ، حتى ولو اخفيت شريط الادوات ولا تُظهر ايقونة الطباعة ، فالمستخدم يستطيع بالنقر على الفأرة باليمين ومن القائمة ان يطبع ، وحتى لو لم اخفيت قائمة النقر بيمين الفأرة ، فالمستتخدم يستطيع ان يضغط على Ctrl + P ويطبع ، فالحل هنا يكون ان: ان تُخفي شريط الادوات ، وان تُخفي قائمة النقر باليمين ، وان تعمل كود يصطاد الضغط على الزر Ctrl فيُلغيه ب- ان تضع صورة مائية على التقرير المعاينة ، تقول فيها مثلا: ان التقرير غير رسمي بغير رقم الوصل ، وهذا الرابط يشرح عمل الصورة المائية: http://www.officena.net/ib/topic/59776-اسئله-عن-التقارير/?do=findComment&comment=387356 2. ان تضع كود خاص بالوندوز (وليس للأكسس) ، بحيث عند اعطاء امر الطباعة ، فنتدخّل ونعطي رقم الوصل ، ثم نسمح للوندوز ان تطبع التقرير جعفر
-
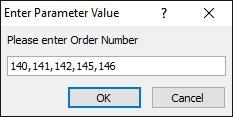
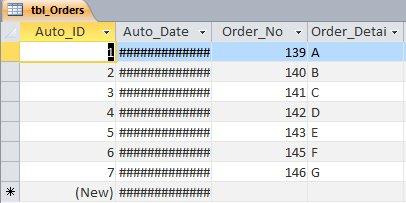
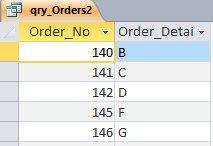
السلام عليكم هذه طريقتي الجدول: . الاستعلام: معادلة Evalفي الاستعلام يجب ان تكون هكذا: 1. اسم الجدول ، 2. اسم الحقل ، 3. الامر IN ، 4. المسمى الذي يظهر لنا في النافذة ، حتى نُدخل في البيانات المطلوبة للمعيار (لاحظ الصورة التي بعد هذه الصورة) . وهذا هو الكود: Eval([tbl_Orders]![Order_No] & " In(" & [Please enter Order Number] & ")") هكذا يجب ان تُدخل المعيار ، وبإستخدام الفاصلة بين الارقام: . والنتيجة: . جعفر 279.More_Than_One_Condition.accdb.zip
-
يا رجال ، مب الكل يفهمها وهي طايرة ، ترى احنا على قدنا لو من البداية شرحت شوي زيادة ، وبالخصوص مع هالصورة ، لكان السؤال واضح جدا الطريقة الاسهل اللي تيجي على بالي هي انك لا تسمح بمعاينة التقرير ، وانما تطبعه مباشرة (وفي الواقع المعاينة مهمة لأغراض معينة ، ولكن لمعظم التقارير ، فيجب طبعها مباشرة) ، عن طريق هذا الكود: DoCmd.OpenReport "Name_All", , , "[Num]=" & Forms!Name_all!Num . جعفر
-

VBA CODE error Invalid procedure call or argument
jjafferr replied to مى الكيال's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
ما شاء الله ، هذا الموضوع مبارك ، فقد شاركنا فيه الاستاذ رمهان ايضا بعد غياب طويل يا رجال وينك من زمان جعفر -
وعليكم السلام يا ريت لو تعمل بحث قبل ان تضع سؤالك ، فالمنتدى غني بمثل هذه المواضيع تفضل هذا الرابط مثلا: http://www.officena.net/ib/topic/66974-البحث-في-الانترنت-من-نموذج-الاكسس-عنوان-معدل/?do=findComment&comment=435559 جعفر
-
وعليكم السلام لأن Num حقل رقمي ، الكود الصحيح هو (لاحظ ، لا توجد مسافة فاضية في نهاية السطر من اليمين): DoCmd.OpenReport "Name_All", acViewPreview, , "[Num]=" & Forms!Name_all!Num او DoCmd.OpenReport "Name_All", acViewPreview, , "[Num]=" & Me.Num جعفر 277.ترقيم.mdb.zip
-

ما هى طريقة معرفة رقم الصفحة بالتقرير
jjafferr replied to أبو عبدالله الحلوانى's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
حياك الله ، وشكرا على هالكلمات الجميلة -

VBA CODE error Invalid procedure call or argument
jjafferr replied to مى الكيال's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
وعليكم السلام ورحمة الله وبركاته انا اقول اليوم من الصبح فرح وسرور ، اثاريه مقدمة لقدوم الغالية الدكتورة أم عهود والله لك وحشة ، ولازالنا نسميك الغائبة الحاضرة ، فلمساتك في كل مكان ، وهي صدقة جارية لك بإذن الله تعالى اسعدتيني بوجودك معانا بعد هالغيبة الطويلة جعفر -

VBA CODE error Invalid procedure call or argument
jjafferr replied to مى الكيال's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
رجاء ارفاق قاعدة بياناتك -

VBA CODE error Invalid procedure call or argument
jjafferr replied to مى الكيال's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
السلام عليكم اختي انتي لديك هذه الاسطر: Dim appword as word.application Dim doc as word.document فهذا معناه انك يجب ان تختارين: VBA > Tools > Reference > Microsoft Word xx.x object Library فهل تم اختيار المرجع اعلاه؟ الطريقة الاخرى التي تستطيعين استعمالها ، وبدون الرجوع لمرجع ، هي تغيير هذه الاسطر بالتالي (ولكن بعض الاوقات بعض الاوامر في الكود لن تعمل بهذه الطريقة): Dim appword as object 'word.application Dim doc as object 'word.document جعفر -
السلام عليكم وتأييدأ لأخي أبوخليل ، وإيضاحا بالصور: http://www.officena.net/ib/topic/66616-لصق-ارتباط/?do=findComment&comment=433253 جعفر
-
السلام عليكم المعادلة على كون Num رقم او نص: رقم DoCmd.OpenReport "Name_All", acViewPreview, , "[Num]=" & forms!Name_All!Num نص DoCmd.OpenReport "Name_All", acViewPreview, , "[Num]='" & forms!Name_All!Num & "'" جعفر
-
آسف أخوي أبو وليد ، بس هذا الكود لا علاقة له بالموضوع هذا وانا بعيد عن كمبيوتري الاصل ، فما اعرف وين الكود الاصل علشان اقارن بينهم اقترح عليك ان تفتح سؤال جديد ، وتعرض الكود الاصل ، ثم تعرض الكود الجديد ، فمنه نستطيع ان نعمل المقارنة ، كذلك يُحبذ ان ترفق بيانات قليلة في برنامجك ، وترفعه كذلك والاهم انك تذكر رابط الموضوع الاصل ، حتى يكون سهل على المتتبع هذا الموضوع يُغلق
-
وعليكم السلام أخي عمرو ماشاء الله عليك ، وللامام ان شاء الله بس للأسف في بطئ / تأخير في الكود انت كلما قلت if ثم endif ، فالكود يقوم بفحص كل if (لا يقرأ اي كود بين الجملتين ، اذا لم يتحقق الشرط) ، مما يعني ان البرنامج سيتحقق في 4 if في الكود الذي عملته انت ، بينما لو عملت if ثم elseif ثم elseif ثم .... ثم else ثم endif ، فإن البرنامج سيفحصه كله مرة واحدة فقط ، حيث ان if و elseif و else تُعتبر شرط واحد اليك طريقتين بدل الكود الذي استعملته انت: Function Con(x) If Mid(x, 1, 1) = "0" Then Con = Mid(x, 2, 15) ElseIf Mid(x, 1, 2) = "00" Then Con = Mid(x, 3, 15) ElseIf Mid(x, 1, 3) = "000" Then Con = Mid(x, 4, 15) ElseIf Mid(x, 1, 4) = "0000" Then Con = Mid(x, 5, 15) Else Con = Replace(x, " ", "") End If End Function او Function Con(x) If IsNumeric(x) = True Then For i = 1 To 4 If Mid(x, i, 1) = 0 Then Con = Mid(x, i + 1, 15) Else Exit For End If Next i Else Con = Replace(x, " ", "") End If End Function جعفر
-

هدية: البحث عن اي جزء من الكلمة ، في اي عدد من الحقول
jjafferr replied to jjafferr's topic in قسم الأكسيس Access
السلام عليكم وجدت هذا المثال ، البحث في عدة حقول ، وبين تاريخين ، فاحببت مشاركتم فيه: http://allenbrowne.com/ser-62.html والمرفق من هنا http://allenbrowne.com/binary/Search2000.zip جعفر -
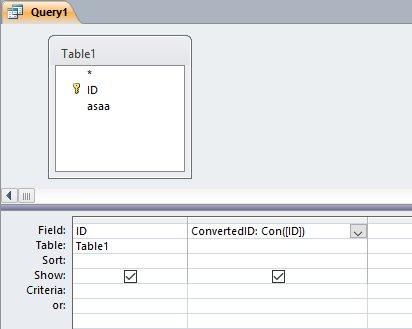
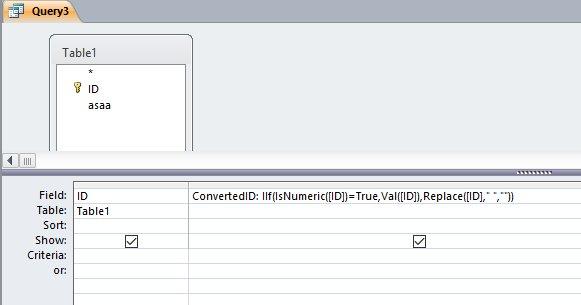
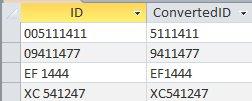
وعليكم السلام بما انك تستخدم الاستعلام مباشرة ، فاليك طريقتين: 1. بإستخدام الوحدة النمطية Con: . وهذه هي الوحدة النمطية: Function Con(x) If IsNumeric(x) = True Then 'رقم Con = Val(x) Else 'نص Con = Replace(x, " ", "") End If End Function . والطريقة الاخرى ، هي وضع الكود كله في الاستعلام ، هكذا: . طبعا التغيير على الكود هنا سيكون اكثر صعوبة من التغيرر في الوحدة النمطية ، والنتائج في كِلا الاستعلامين: . جعفر 276.Test.accdb.zip
-
حياك الله ويُغلق هذا الموضوع